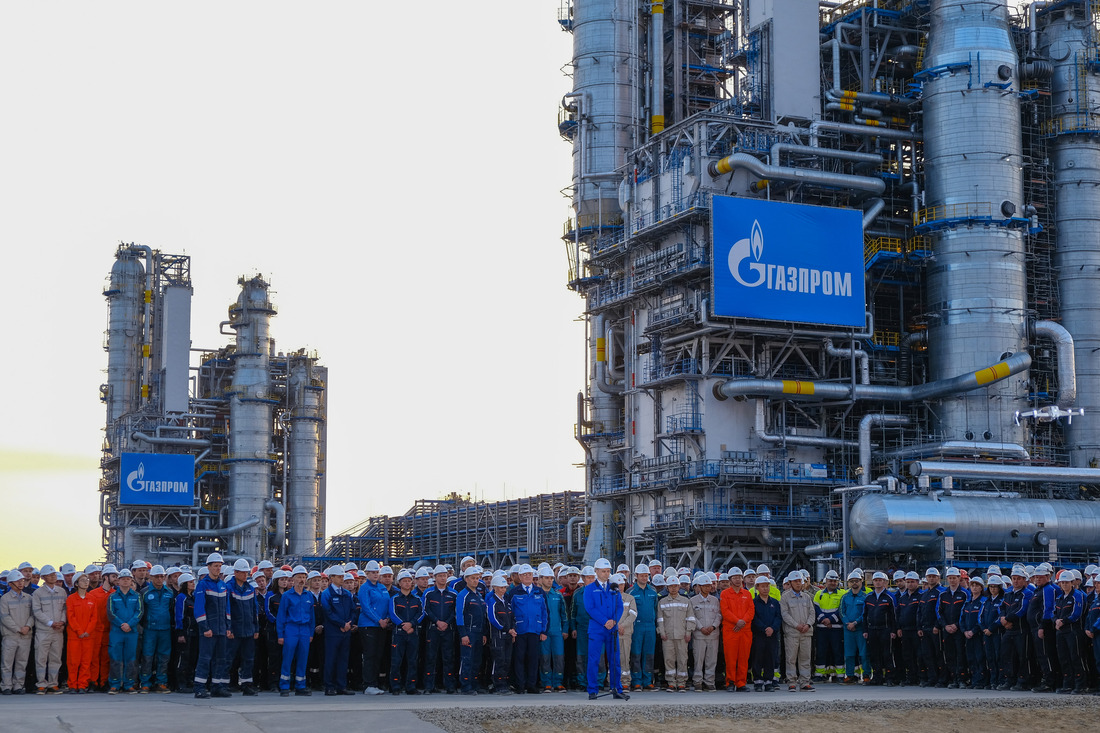
Amur Gas Processing Plant enters operation
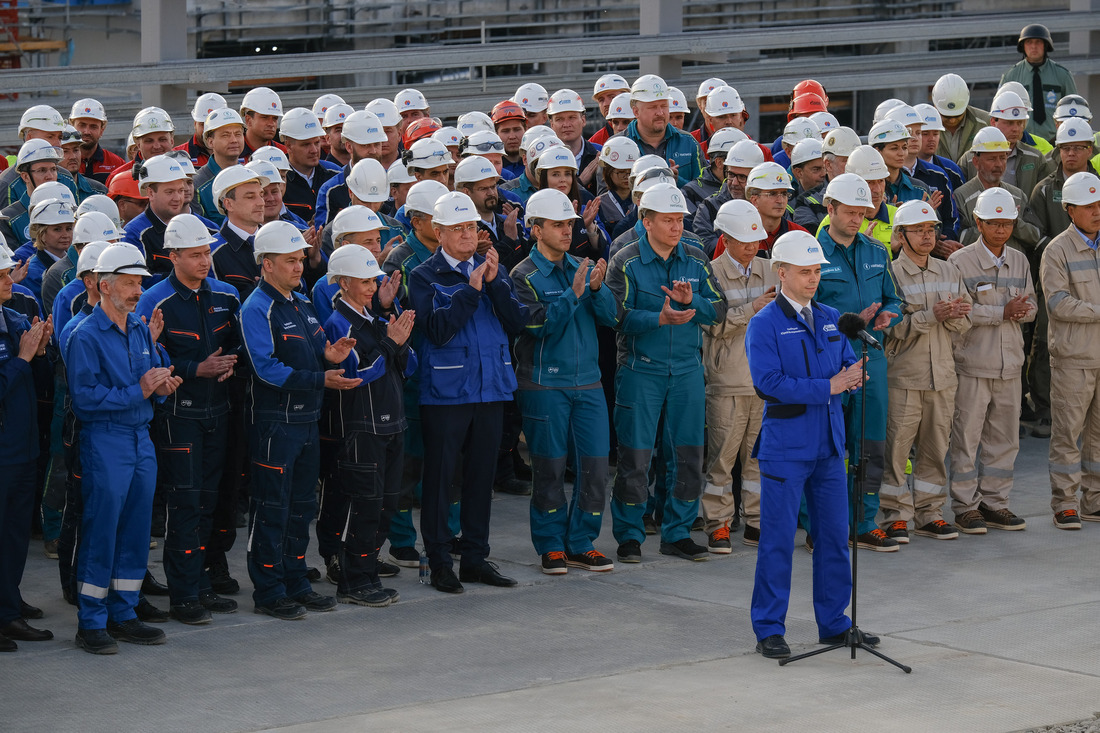
The commissioning ceremony for the first production train of the (GPP), one of the largest plants of its kind in the world, took place today via a video link. The implementation of such an ambitious project in the area of gas processing has no parallel in the history of Russia’s gas sector.
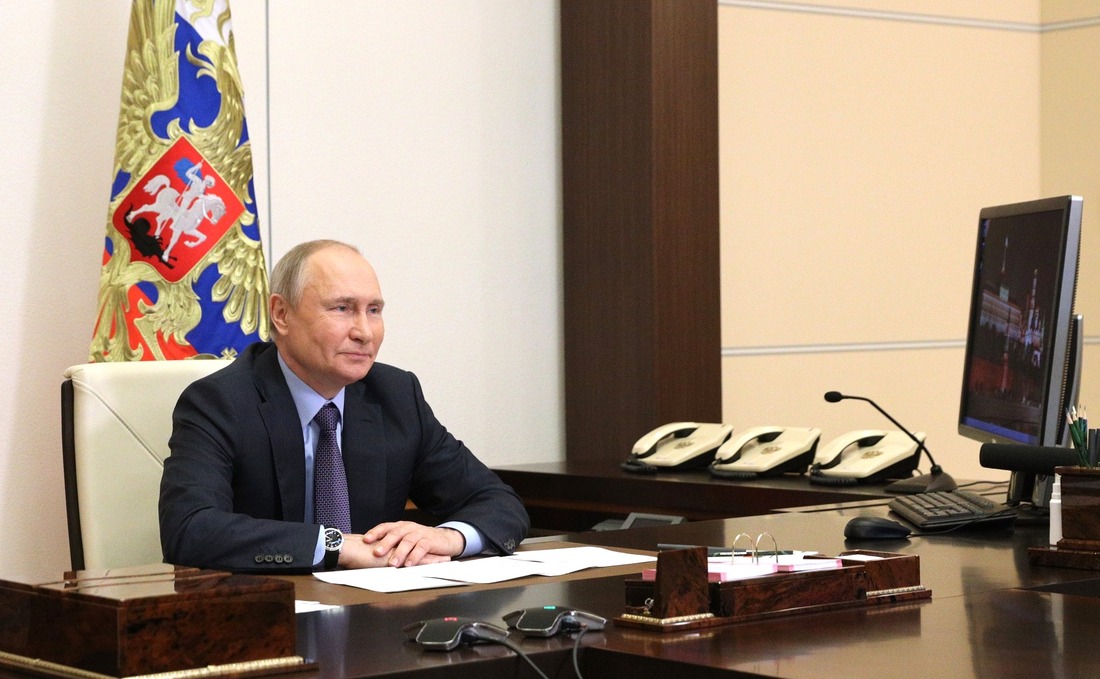
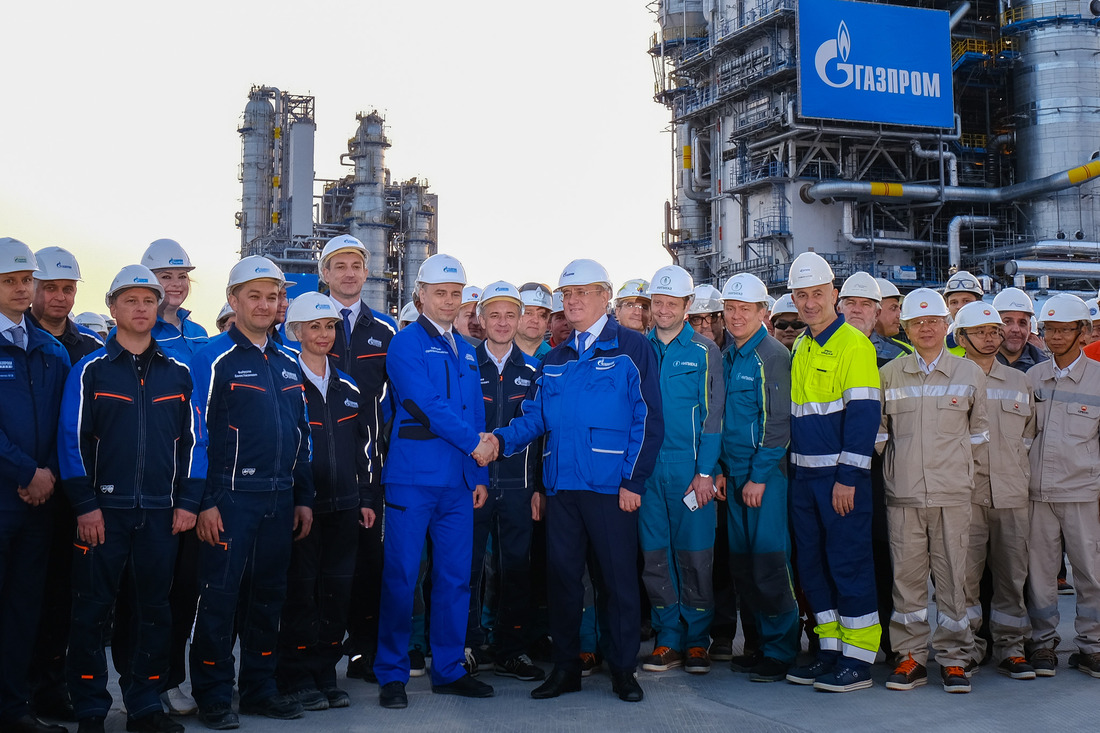
Taking part in the event were Vladimir Putin, President of the Russian Federation, , Chairman of the Gazprom Management Committee, and Vasily Orlov, Governor of the Amur Region.
The Amur GPP is located near the town of Svobodny, Amur Region. With a design processing capacity of 42 billion cubic meters of gas per year, the GPP is going to become the main enterprise for advanced gas processing in Russia’s Far East. The plant receives multi-component gas via the gas pipeline from the (Yakutia); later on, it will also receive gas from the (Irkutsk Region).
Initially, the fundamental principle that underpinned the project was the necessity to process within the Russian Federation the multi-component gas fed from Power of Siberia.
The construction of the first production train of the Amur GPP was finished strictly on schedule. The commissioning of the next five trains is synchronized with increases in the volumes of gas transmitted via Power of Siberia. In 2025, the GPP will reach its full design capacity.
The products of the Amur GPP include sales gas (methane) and the components extracted from this gas, which are valued in the gas chemical and other industries. Operating at full capacity, the GPP will use cutting-edge equipment and state-of-the-art cryogenic technologies to produce 2.4 million tons of ethane, 1.5 million tons of liquefied petroleum gases (LPG), and 200,000 tons of pentane-hexane fraction. The primary consumer of the GPP’s ethane and LPG will be the Amur Gas Chemical Complex (a joint project of SIBUR and Sinopec).
One of the main products of the Amur GPP is helium, a particularly sought-after element for high-tech industries. With an annual output of 60 million cubic meters, the GPP is poised to become the global leader in helium production. The key link in the logistics chain of helium supplies to the international market will be the helium HUB near Vladivostok, which is going to be put in operation in the nearest future.
Gas processing with high value-added products is increasingly gaining importance in Gazprom’s development strategy. After the Amur GPP reaches its design capacity, the share of gas processing in the total volume of revenue will grow substantially along with the Company’s profits. This will help balance the influence of the price environment on Gazprom’s businesses and improve the economic efficiency of the Company’s expansive production complex in its entirety.
“The Amur GPP is one of the most cutting-edge and high-tech production enterprises in the world. Its construction schedule was extremely tight. Less than six years passed between the first pile and the start-up. An unprecedented amount of work was completed in that period. Today, the Amur Gas Processing Plant is onstream, and it has already become an integral part of Gazprom’s unified production system,” said Alexey Miller.
Background
The construction of the Amur GPP in October 2015. (part of the Gazprom Group) is the investor, customer, and operator for the Amur GPP. Construction management is carried out by NIPIGAZ (part of the SIBUR Group). The core process equipment for cryogenic gas separation is provided by Germany’s Linde. Products of Russian machine-building enterprises are also used at the GPP. In St. Petersburg, the production of spiral heat exchangers was launched for the first time in Russia so as to provide for heat recovery of nitrogen-helium mixture during the helium production process at the Amur GPP.
Some 1,000 equipment suppliers and over 500 contracting organizations were engaged in the project. About 35,000 construction workers are currently at the Amur GPP’s construction site. The number of permanent jobs at the GPP will total around 3,000.
In December 2019, the project financing deal for the overall amount of EUR 11.4 billion was for the Amur GPP construction project. The funds are being provided by 22 banks from Europe, Asia, and Russia (Gazprombank, SberBank, VTB Bank, Otkritie Bank, and VEB.RF). The deal was unprecedented in Gazprom’s history and became one of the largest transactions of this kind in Europe over the last few years.
Extensive infrastructure was created for the construction of the Amur GPP: 27 kilometers of access roads, a wharf of the Zeya River, some 40 kilometers of railway tracks, and three camps for shift workers, which are also used in associated investment projects.
Process steam and electric power are generated by the Svobodny Thermal Power Plant, which was into operation by Gazprom in the spring of 2021.
The region’s social infrastructure is evolving as well. A residential microdistrict for the workers of the Amur GPP is being built in the town of Svobodny. The microdistrict has apartment houses, an outpatient clinic, a kindergarten, a school, a sports center, a cultural center with a concert hall, and a children’s art center.
Chayandinskoye is one of the largest fields in eastern Russia and the basis for the Yakutia gas production center. The field is unique in terms of its recoverable gas reserves (1.2 trillion cubic meters). It has the annual design output of 25 billion cubic meters of gas. The field came onstream in 2019.
The Kovyktinskoye field, which has the largest gas reserves in eastern Russia, is the basis for the Irkutsk gas production center. The field is unique in terms of its recoverable gas reserves (1.8 trillion cubic meters). It has the annual design output of 27 billion cubic meters of gas. Work is underway to prepare the field for full-scale production.
The two fields form the resource base for the Power of Siberia gas pipeline, which started conveying gas from Chayandinskoye in 2019. A pipeline section from Chayandinskoye to Kovyktinskoye is currently under construction.







Enlarged photo (JPG, 970 KB)